200以上 derivative of ln(x^2 y^2) with respect to x 168562-Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x

How Do You Differentiate Y Sin X 6 Tan X 2 X 2 2 2 Socratic
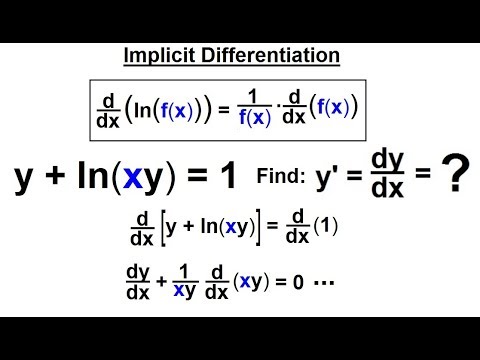
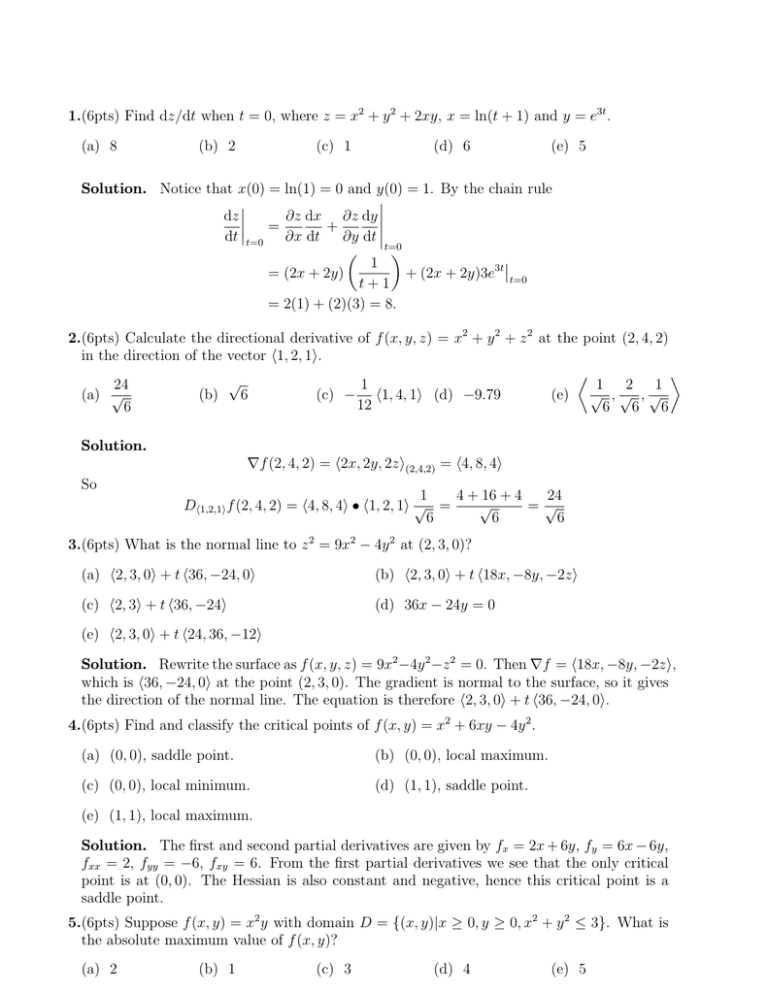
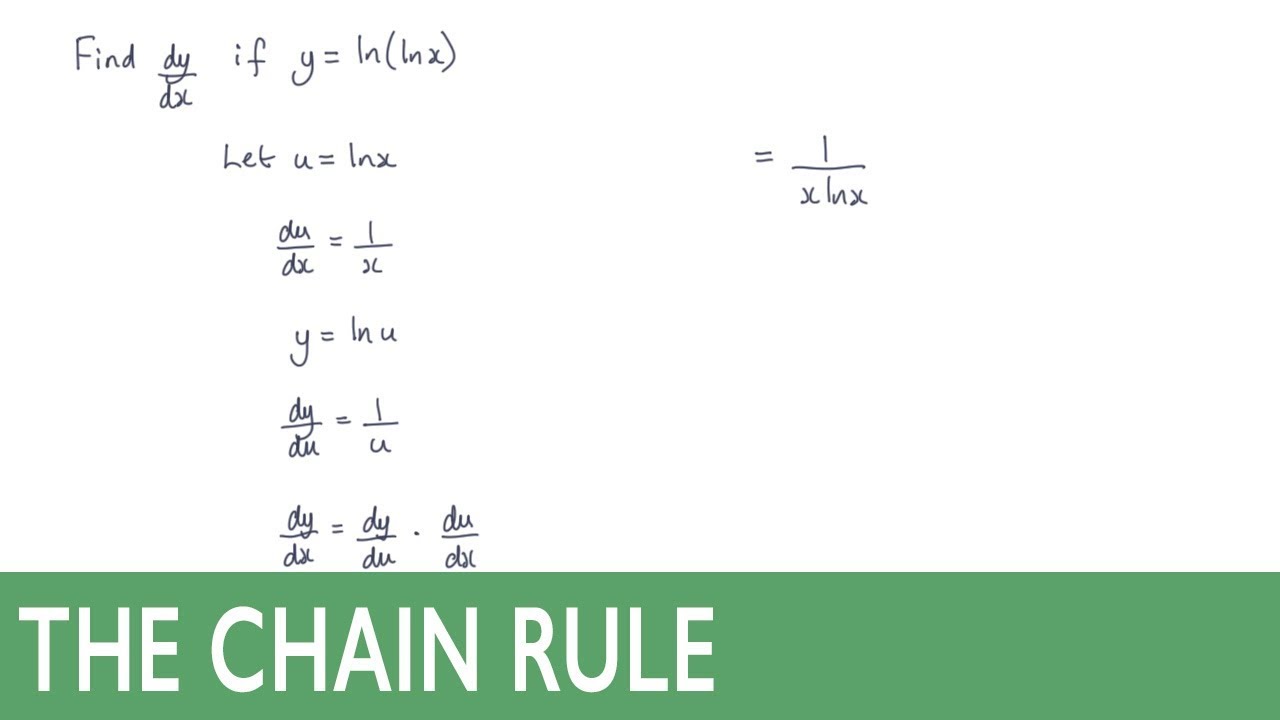
Answer to find the derivative of y with respect to x, t, ore 1 y = In(In(ln x)) 2 y = 0(sin(ln 0) cos(ln 0)) 3 x(x1)(x2) V(x1)(2x3) 3 y = 4 y = e(vx²) 5 y = SolutionInnYou can use Implicit differentiation to differentiate x 2 y 2 x y 2 = x y wrt x With implicit differentiation you differentiate each term on the both sides using standard rules If you encounter a y this becomes d y d x if you have a y 2 use the chain rule to get 2 y d y d x 2 x y x 2 d y d x 2 y 2 4 x y d y d x = 1 d y d x Rearrange
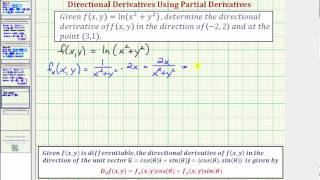
Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x
Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x-1 Find the derivative, with respect to x, of each of the following functions (in each case y depends on x) a) y b) y2 c) siny d) e2y e) xy f) xy g) ysinx h) ysiny i) cos(y2 1) j) cos(y2 x) 2 Differentiate each of the following with respect to x and find dy dx a) siny x2 4y = cosx b) 3xy2 cosy2 = 2x3 5 c) 5x2 − x3 siny 5xy = 10Differentiate with respect to x d dx (x 2) d dx (y 2) = d dx (r 2) Let's solve each term Use the Power Rule d dx (x2) = 2x Use the Chain Rule (explained below) d dx (y2) = 2y dy dx r 2 is a constant, so its derivative is 0 d dx (r2) = 0 Which gives us
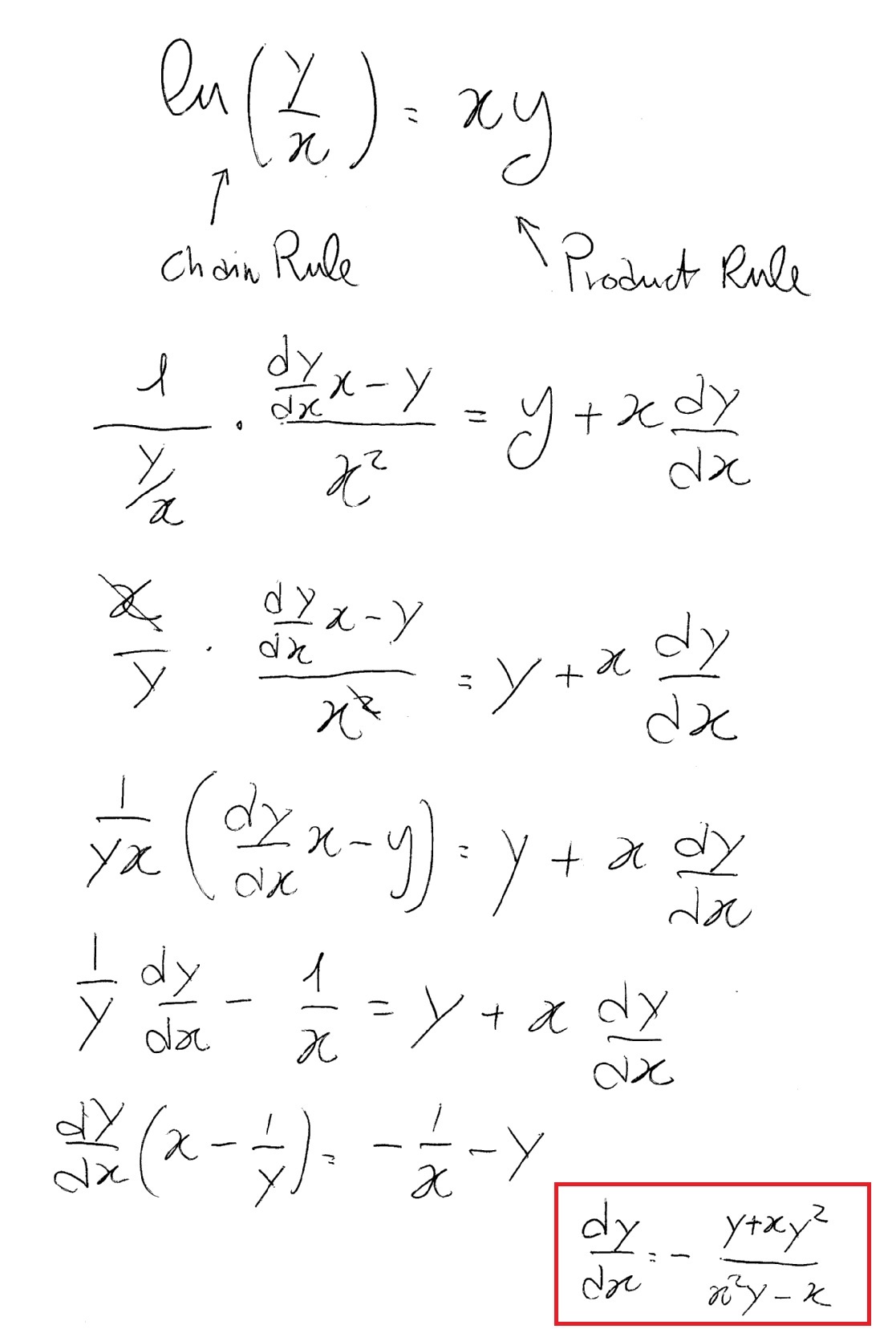
How Do You Differentiate Ln Y X Xy Socratic
X x x^x xx, use the method of logarithmic differentiation First, assign the function to y y y, then take the natural logarithm of both sides of the equation y = x x y=x^x y = xx 3 Apply natural logarithm to both sides of the equalityDifferentiate a x with respect to x You might be tempted to write xa x1 as the answer This is wrong That would be the answer if we were differentiating with respect to a not x Put y = a x Then, taking logarithms of both sides, we get ln y = ln (a x) so ln y = x lna So, differentiating implicitly, we get (1/y) (dy/dx) = lna and so dy/dx = y lna = a x lnaThe point (−2,4) lies on the curve in the xyplane given by the equation f(x)g(y)=17−x−y, where f is a differentiable function of x and g is a differentiable function of y Selected values of f, f′, g, and g′ are given in the table above What is the value of dydx at the point (−2,4) ?
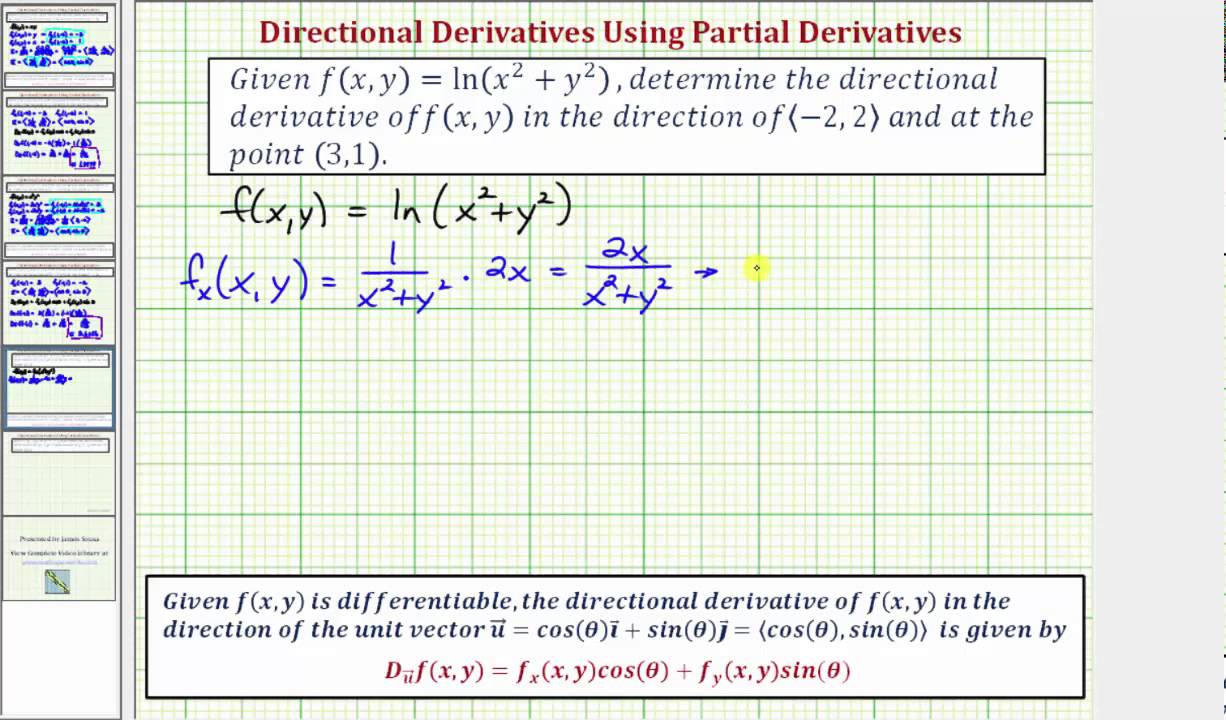
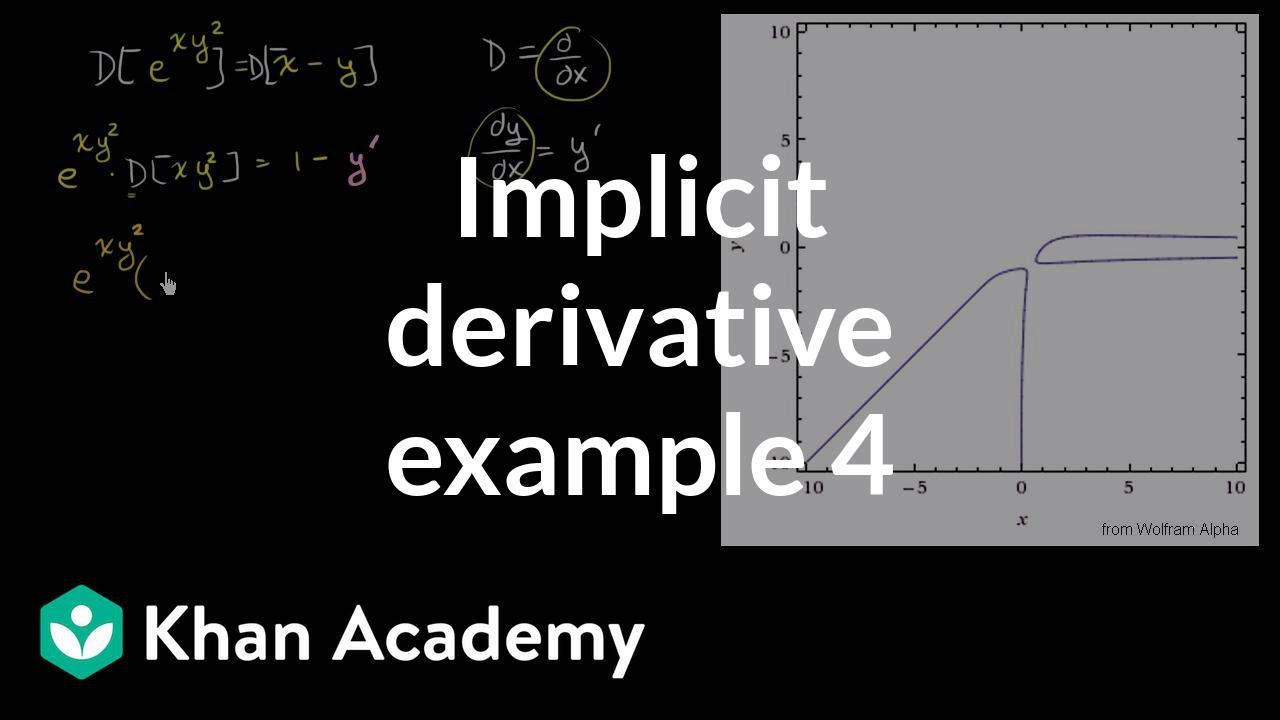
So let's do that The derivative of both sides with respect to x, do a little bit of implicit differentiation Really just an application of the chain rule So, on the lefthand side right over here, this is going to be the derivative of e to the y with respect to y, which is just going to be e to the y times the derivative of y with respect toLet's first think about a function of one variable (x) f(x) = x 2 We can find its derivative using the Power Rule f'(x) = 2x But what about a function of two variables (x and y) f(x, y) = x 2 y 3 We can find its partial derivative with respect to x when we treat y as a constant (imagine y is a number like 7 or something) f' x = 2x 0 = 2xDerivative Here, n = 4 d/dx
Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to xのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
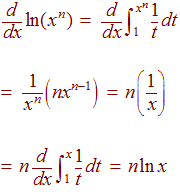 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
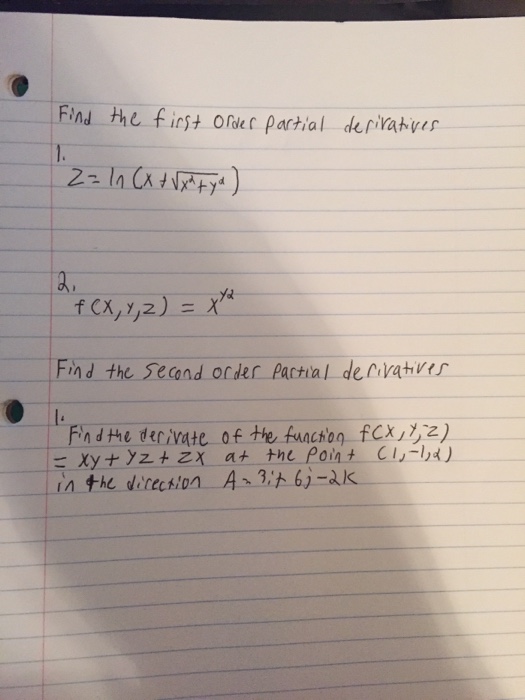 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | 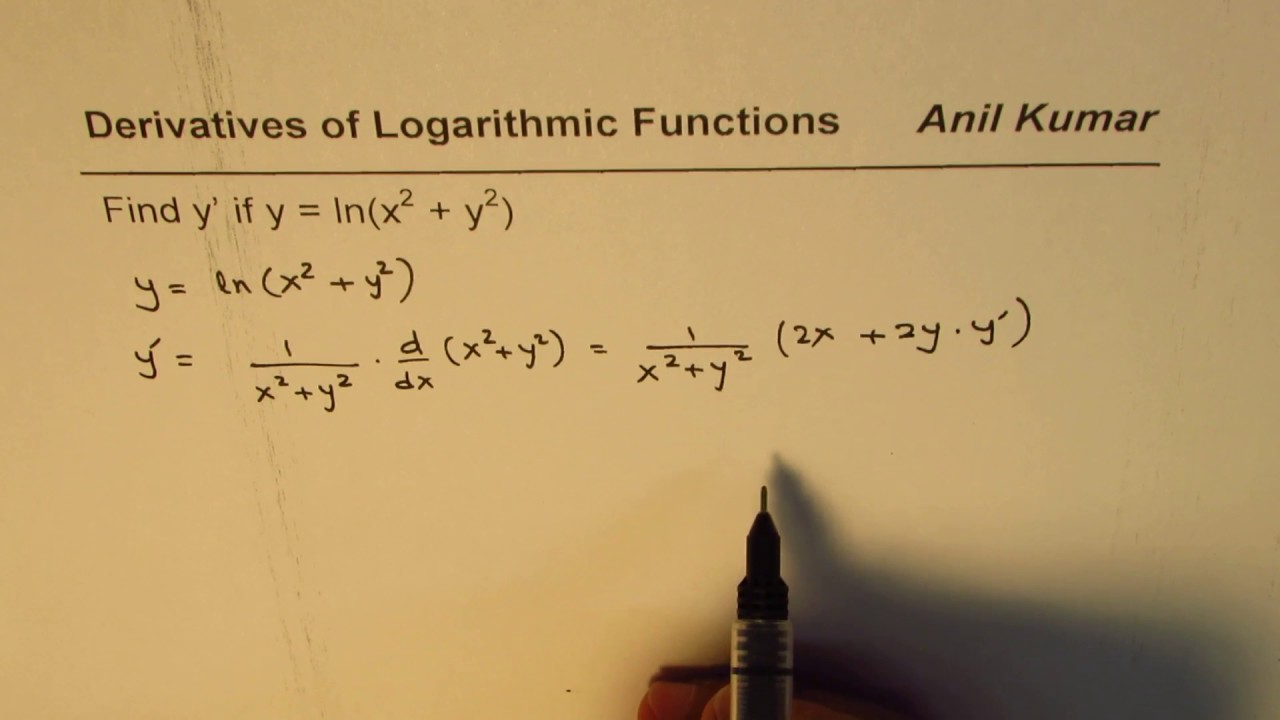 |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | 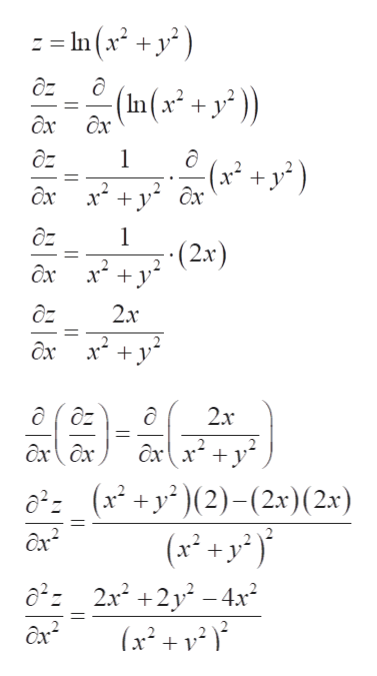 |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | 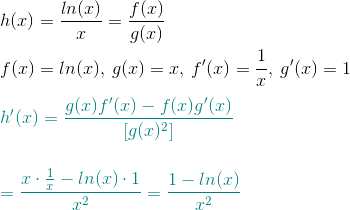 |
 |  |  |
「Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 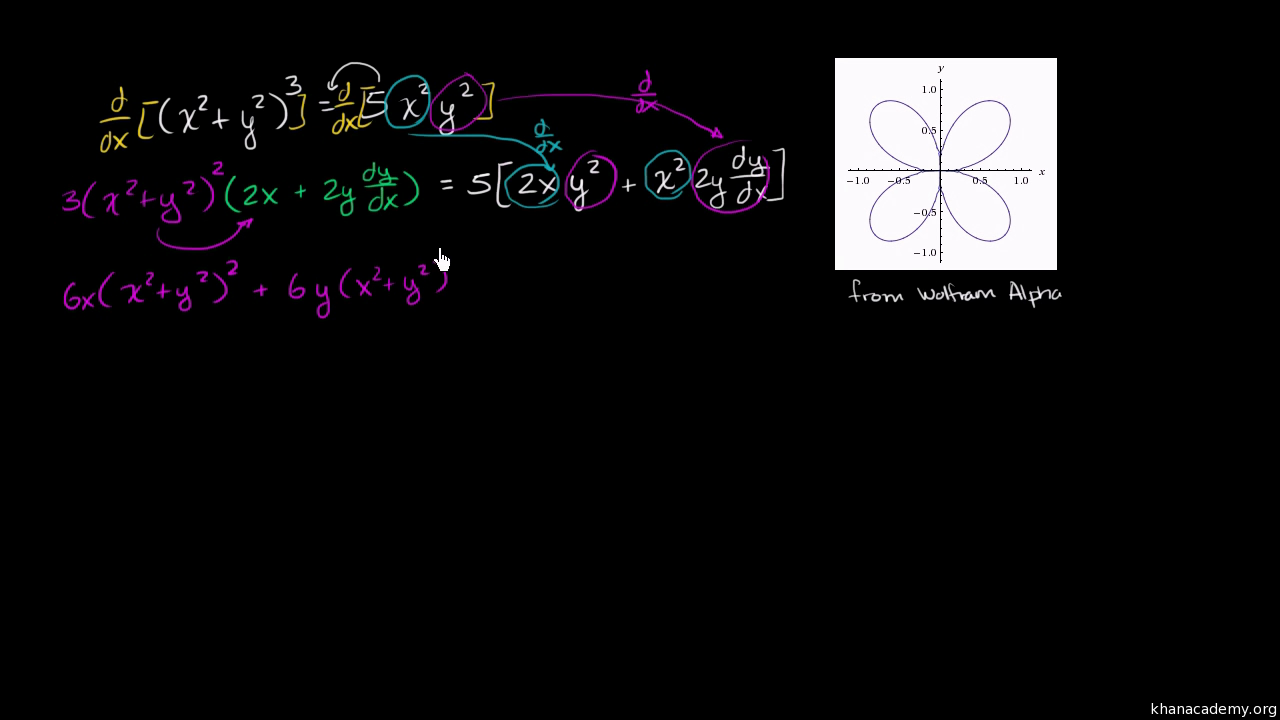 | |
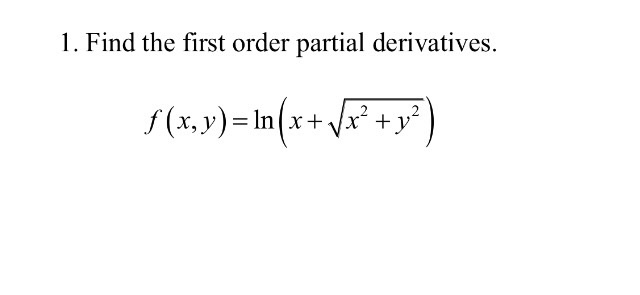 | 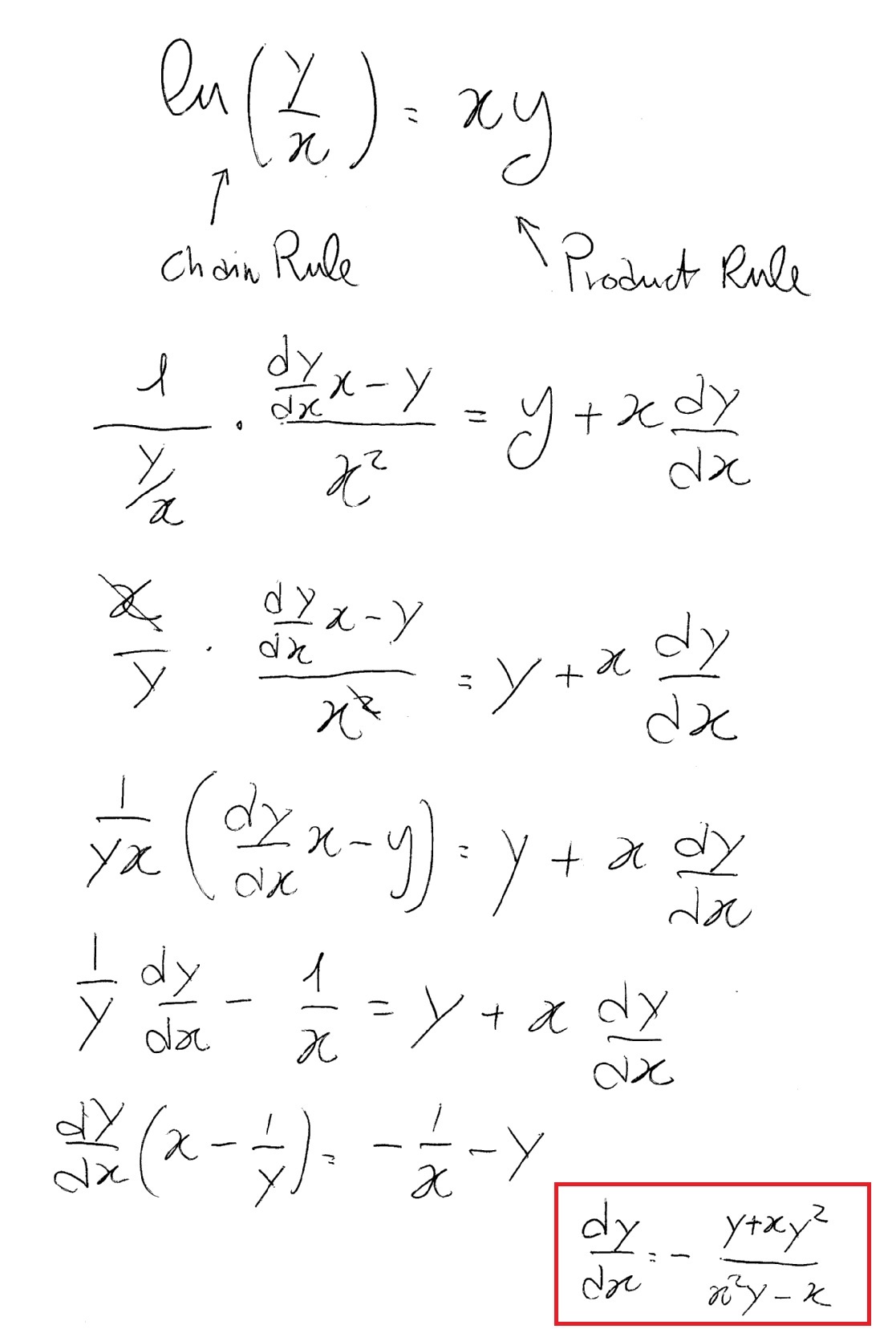 | |
 |  |  |
「Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
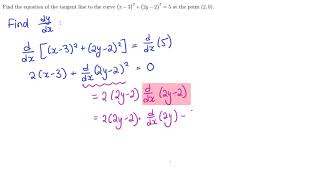 |  | |
 |  |  |
 | 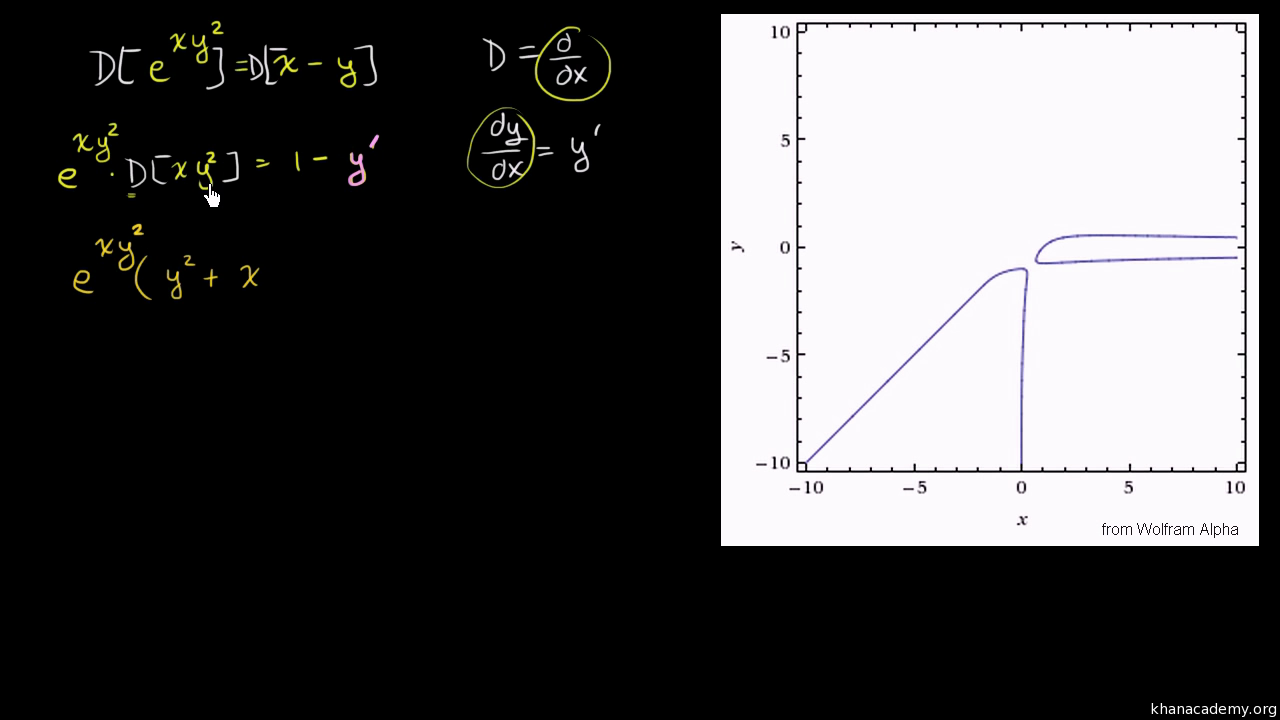 | |
「Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
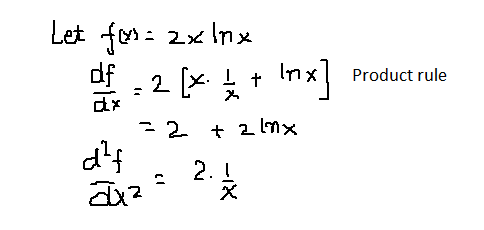 | 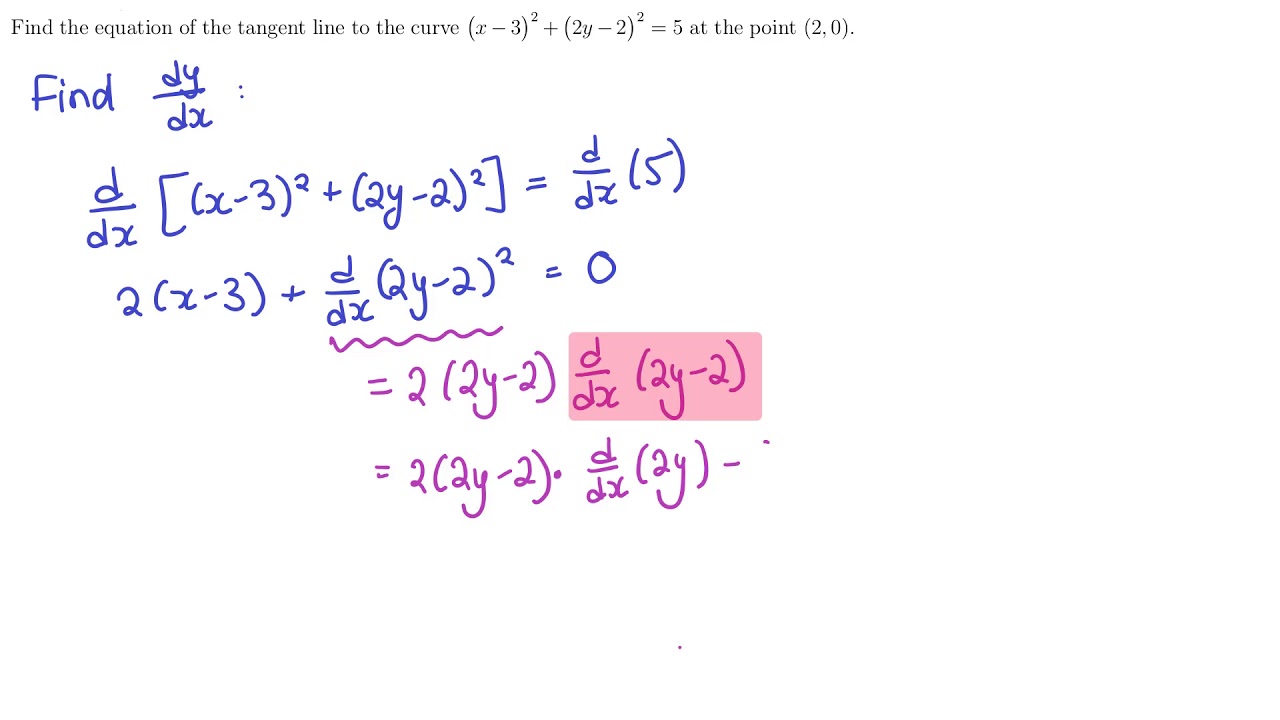 |  |
 | ||
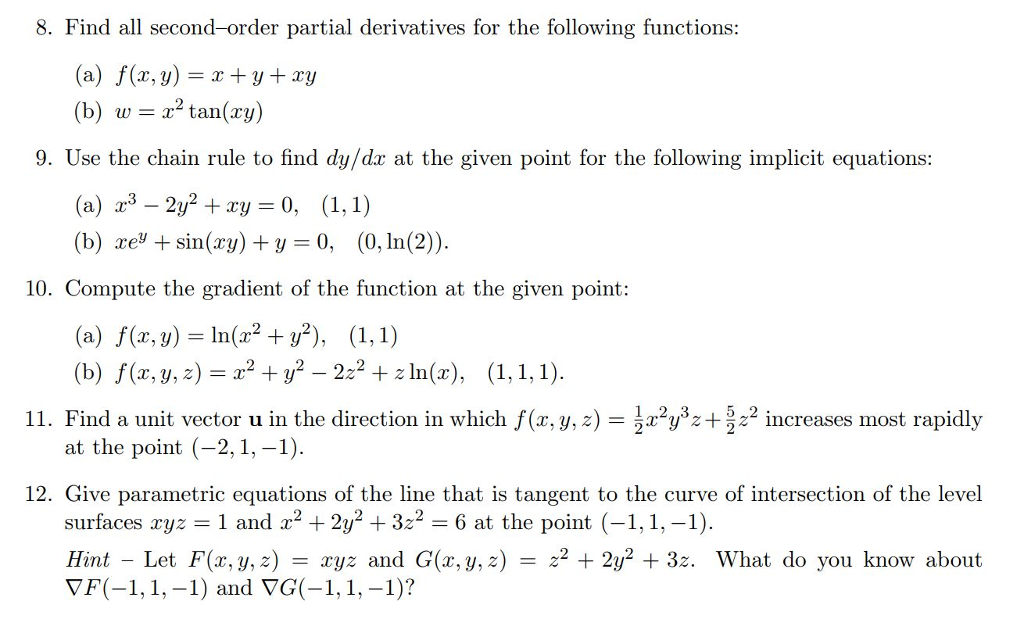 |  | |
「Derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
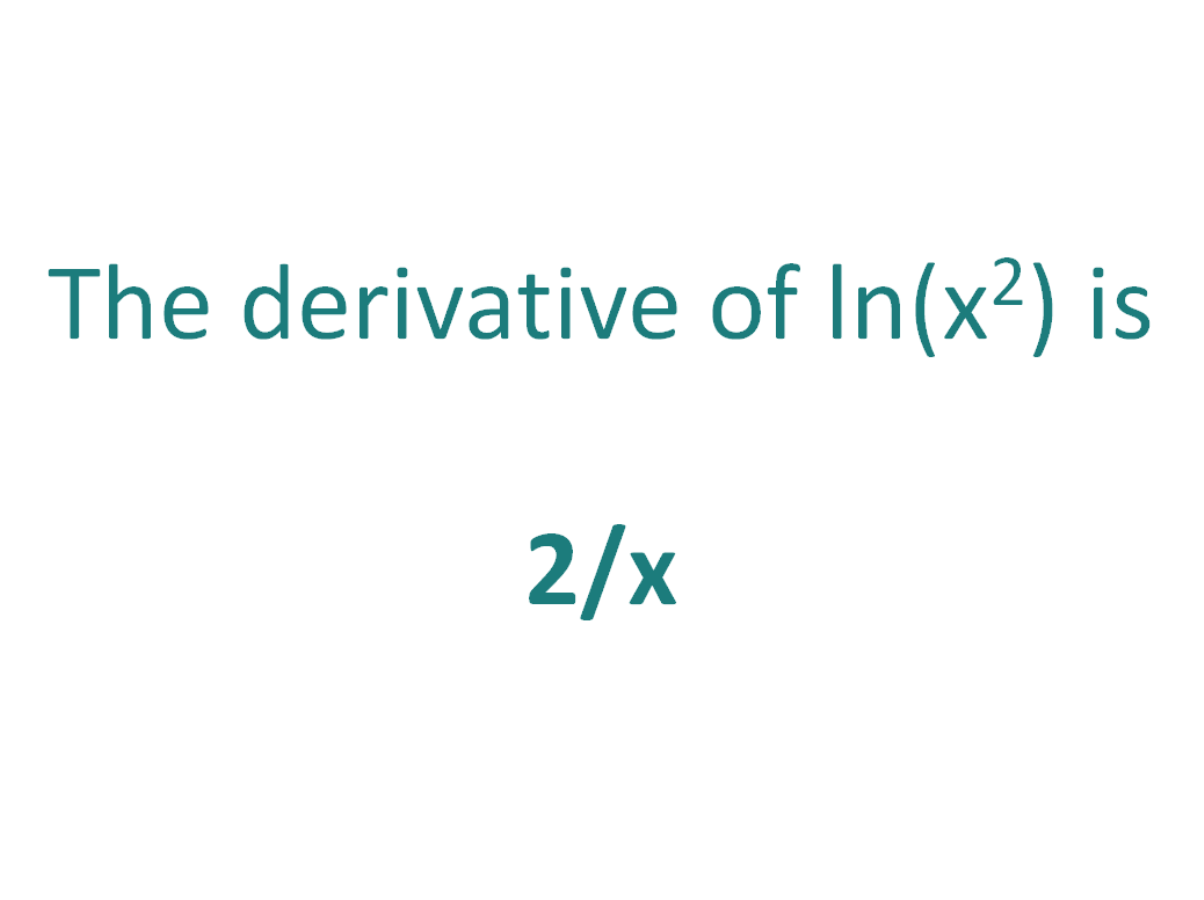 | 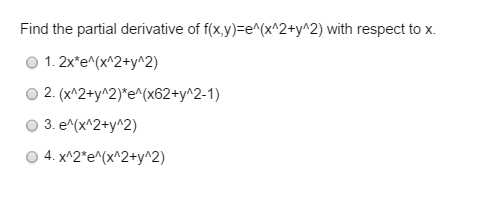 |
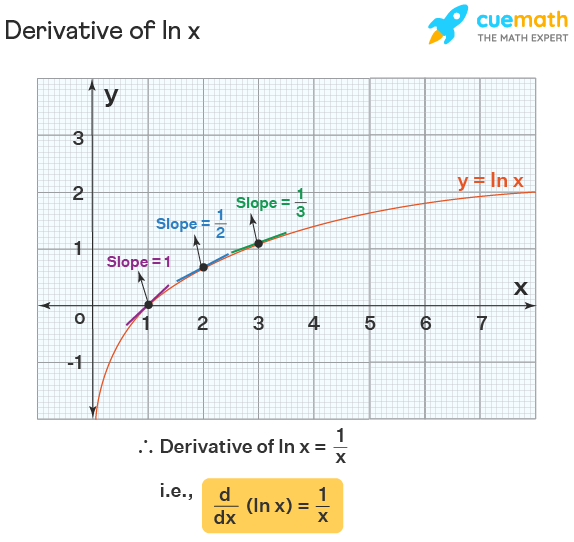
Implicit\derivative\\frac {dy} {dx},\ (xy)^2=xy1 \frac {\partial} {\partial y\partial x} (\sin (x^2y^2)) \frac {\partial } {\partial x} (\sin (x^2y^2)) derivativecalculator en Sign In Sign in with Office365 Sign in with Facebook ORExample 2 Find the derivative of ln x 2 Solution Let f(x) = ln x 2 We can find its derivative in two methods In each of these methods, we are going to use the fact that "the derivative of ln x is 1/x" Method 1 We have ln a m = m ln a So f(x) = 2 ln x Its derivative is, f'(x) = 2 d/dx(ln x) = 2 (1/x) = 2/x Method 2 By chain rule,
Incoming Term: derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x, partial derivative of ln(x^2+y^2) with respect to x,




コメント
コメントを投稿